Deuterium Depleted Water Health Benefits: A Superior Sip?
The importance of drinking at least 6-8 glasses of water per day for hydration and health benefits are well known and accepted. In recent times, however, there has been a movement suggesting that deuterium depleted water (DDW) may be superior to any plain old water. Deuterium depleted water has claimed to have a number of other extraordinary health benefits, including: anti-cancer properties, enhanced cell growth and recovery, detox and metabolism, improved mood and brain function, and protection for the liver and heart.
There are a number of deuterium depleted water products on the market. The sample I looked at online ranged in price between approximately A$5/litre for barely depleted water, up to approximately A$28/litre (excluding postage). Personally, I’d have to be darned sure it lived up to all the hype if I were to spend such an amount on water. Let’s see what makes DDW so different and what the research says about its powers…
Key Points:
- All water naturally contains deuterium, but higher deuterium concentrations produce a slower rate of biochemical reactions compared to waters lower in deuterium.
- A bulk of animal and cell culture studies suggest deuterium depleted water may suppress tumour growth. The human evidence is equivocal. Much work needs to be done first of all to confirm anti-cancer effects, and second to ascertain how DDW can be effectively used in different cases.
- There is modest evidence that deuterium depleted water may also enhance cell growth, metabolism and antioxidant activity, and have benefits to brain function. There is limited evidence of a potential role in heart health.
- Further deuterium depletions do not necessarily mean greater benefits. It’s more likely that there is an ‘optimal range’ for deuterium levels, and that this range could vary based on an individual’s specific health needs.
Overall, the body of evidence currently appears promising but inadequate. A moderate deuterium depletion of water may assist some in cancer treatment, in improving cell metabolism, growth and repair, improving our brains, and protecting organs such as our heart.
Waters ain’t waters: what is deuterium depleted water?
First, a quick trip down fundamental-science-lane…
Water is also referred to as H2O because each water molecule is made of two Hydrogen (H) atoms and one Oxygen (O) atom.

Each element can be found in different forms or ‘isotopes’. You’re probably familiar with isotopes in the context of radioactivity. However, an isotope is simply an atom of an element with a different number of neutrons in its nucleus, so there are many non-radioactive isotopes.
Hydrogen atoms in their ‘normal’ form has one proton and zero neutrons in its nucleus, plus one electron. Deuterium is an isotope of hydrogen which has one neutron in its nucleus in addition to the proton.
Image credit: This file is an image owned by Fox or another Fox show, most probably The Simpsons. The file’s use qualifies as fair use under United States copyright law. https://simpsons.fandom.com/wiki/Tito?file=Tito.jpg
Bodies of water naturally contain water molecules with deuterium atoms, as well as ‘normal’ hydrogen. Some literature claims natural waters have a deuterium content of about 145ppm, but there in fact can be significant variation across the planet (the waters in some locations having twice the content of others). The changes in the seasons also bring deuterium content variations. There appears to be less variation in the deuterium content of bottled mineral waters (typically in the range of 135-158 ppm).
Deuterium depleted water (DDW) is made by commercial entities through use of technologies such as fractional distillation, or a system that causes hydrogen and oxygen atoms to combust and react. Home distillers are available but the level of depletion they create is insignificant.
Deuterium levels can alter the chemical properties of water.
… So what?
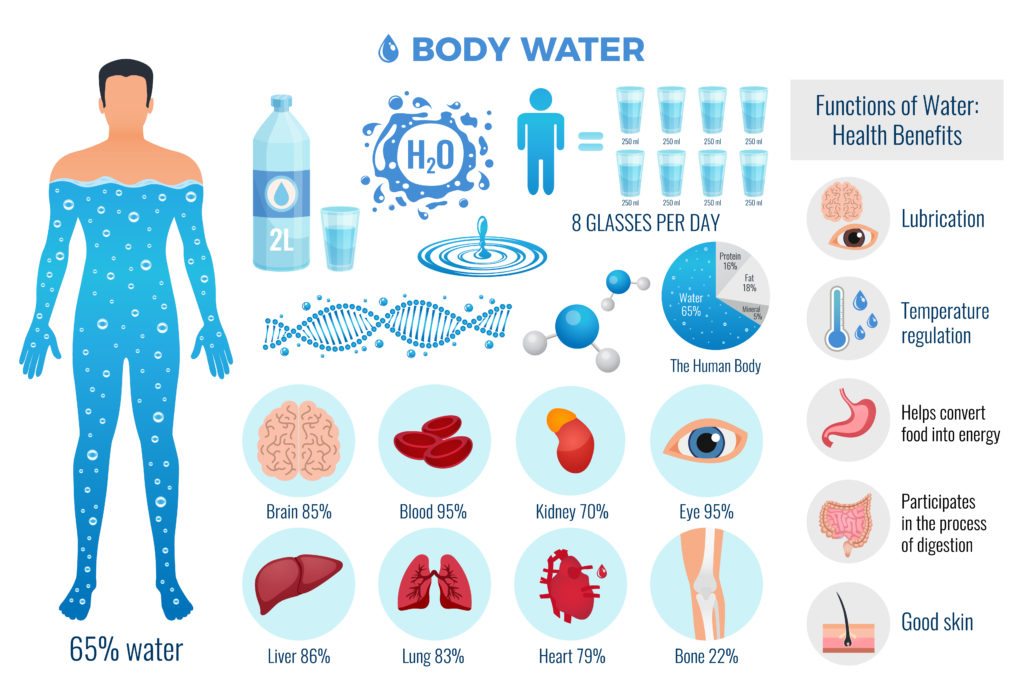
You might care about deuterium because most of your body’s biochemical reactions occur within water, what with you being made of 50-75% water and all. Water of higher deuterium content produces a slower rate of biochemical reactions compared to water lower in deuterium. Thus higher deuterium also inhibits metabolic and physiological processes, growth and development.
Image credit: Food vector created by macrovector – www.freepik.com
It would seem obvious that the composition of water within your body mirrors the water you drink. But, this is not quite true. Water is also produced through metabolic reactions. This means the deuterium content of the fuels you metabolise also contributes to your aqueous make up. This metabolic water accounts for 7-56% of the water content of different mammals. Nonetheless, the easiest way to alter the deuterium content of your body is still through the water you drink.
Benefits of Deuterium Depleted Water
Lowering the deuterium content of your body may increase its functional activity, producing a range of possible benefits:
Cancer-fighting properties
DDW may stunt the proliferation of cancer. It has been shown to inhibit the growth of tumours that have been transplanted from humans into mice. It seems cancer growth may be most effectively inhibited when the body’s deuterium content is progressively lowered (as opposed to suddenly lowered). This is the natural pattern that occurs with continuous DDW drinking. However, a minority of studies have not confirmed the anticancer effect of DDW.
Image credit: Image by skeeze from Pixabay
Encouraging studies have suggested the mechanism of DDW is to accelerate the respiratory chain reaction in the mitochondria of cancer cells. This increases the production of reactive oxygen species, resulting in mitochondrial and cell oxidative stress. The cell attempts to compensate with antioxidant activities, but when this ultimately fails to keep pace there is slower cell growth and reproduction, and, in time, some cell death. Thus it is theorised that DDW may assist the action of antitumour therapies which cause oxidative stress in cancer cells.
In addition, because of the different chemical properties of deuterium to ‘normal’ hydrogen, DDW may speed up the absorption, distribution, use and excretion of medicines.

Most of this information is from animal and cell culture studies. We have limited data from human studies, which suggests increased survival rates and prognosis. At least this is the case in some retrospective studies of patients with lung or breast cancer. Unfortunately the size of these studies varied widely- as did the level of monitoring and control of DDW intake… so we can’t determine what level of deuterium depletion was achieved, or estimate the relationship between this and the response. Furthermore, the studies didn’t have control groups for comparison (instead comparing results to historical records), and it is difficult to ascertain whether other factors may have contributed to the prognoses.
Assuming an anti-cancer effect for humans, there is still some question as to the ideal level of deuterium depletion. Some studies have suggested that DDW becomes most toxic for cancer cells between 50 and 105 ppm deuterium, and that further depletions are less toxic. This levelling out of toxicity is rare (or unheard of) among other anti-cancer agents. In addition, a lab study showed different types of cancer cells (lung, breast, colorectal) had different responses to different levels of deuterium depletion. Thus, any use of DDW would need to be tailored to the patient.
Enhanced cell metabolism, growth and recovery
Stem cells derived from human adipose tissue, and placed in the lab, have been shown to proliferate in cultures with water with 75 ppm deuterium. In addition, their metabolic activity and cell migration rate increased. However, excessive depletion (down to the level of 15ppm) was toxic. A similar result has been seen with human connective tissue cells in DDW solution.
DDW may also strengthen the antioxidant defences of the body. In specific worms who’d previously been subjected to toxicity, DDW activated proteins which help produce antioxidant proteins from DNA, leading to improved lifespan. Also, in rats, DDW treatment has been shown to increase antioxidant activity in red blood cells.
Improved mood and brain function

This claim has had less attention, but DDW may reduce the occurrence of depression. A 2014 paper found a correlation between the incidence of depression in different areas of the USA, and the deuterium content of tap water in those areas. The researchers also conducted tests on mice: those fed DDW had less depressive-like features when in stressful environments, while mice given water with higher than normal deuterium levels had less expression of serotonin transporters (a factor affecting the action of this “happy chemical”).
Also, mice given DDW showed similar responses in their EEG as have been observed in the brains of creatures given certain antidepressants (SSRIs).
Image credit: Background vector created by rawpixel.com – www.freepik.com
It may also help with anxiety: a 2014 paper showed rats given DDW displayed less anxiety-related behaviours in testing scenarios.
Protection of the heart

Evidence of cardioprotective effects is rather limited. One small study of rats showed that DDW resulted in decreased total cholesterol levels and blood fats in rats with normal blood pressure. On the other hand, among rats with pre-existing high blood pressure, DDW feeding was not able to attenuate an increase in cholesterol and blood fats in response to feeding on fructose solution. This indicates the complexity of heart health and the fact that taking care of any singular risk factor alone will likely prove ineffective.
DDW increased blood insulin levels among the rats with normal blood pressure, but countered the increase in insulin levels produced by 15% fructose treatment. It also had non-uniform effects on the activity and presence of the enzymes that produce Nitric Oxide, which relaxes blood vessels and is associated with insulin secretion and glucose control, among other things.
This rat study also suggested there is no significant effect of DDW on blood pressure, regardless of whether blood pressure was initially normal or high.
In summary, limited animal evidence suggests that any cardioprotective effects DDW may have are modified by various other factors. It requires further exploration.
Deuterium Depleted Water: The Verdict
I agree with the recent review by Basov et al., published 15 August 2019, which states that a large amount of research into the benefits of DDW have been published. However, the most impressive evidence tends to be from sources such as worms, rats, bacteria, human cells isolated from the body and treated in the lab. Also, the human studies that we need to draw more robust conclusions could be a way off. In a 2018 paper, Zlatska et al. went as far as to say that “human studies of its effect are impermissible”, as the information on deuterium toxicology is inadequate and/or has not led to a dependable predictive mathematical model of the relationship between laboratory systems and in-body responses. They state that the role of deuterium in our complex bodies is yet to be fully elucidated.
In contradiction to most of the research examined, a review article from 2016 demonstrated that while ‘heavy’ (high-deuterium) water slowed down biological processes among seedlings, yeast and flatworms, it didn’t necessarily cause harm or irreversible changes. It also notes that tolerance to heavy water varies between organisms. Plus, there are claims that both increasing and decreasing deuterium can be beneficial in different circumstances. Heavy water may reduce oxidising molecules that cause tissue damage- in one study fruit flies were given heavy water in early life, with the result that their lifespan increased. Another study showed the effect of a high salt diet on rats’ blood pressure was negated with provision of 25% heavy water. On the other hand, ‘too much’ heavy water can shorten lifespan. Also, the effect of heavy water may change with environmental temperature- at least among some animals. Elsewhere, it has been shown that the lifespan of a certain mushroom was compromised when water contained either excess or deficient deuterium. Yet another study showed human cells could actually adapt to high levels of deuterium: negative effects at 24 hours were followed by reduced toxicity and increased metabolic activity and growth potential by 72 hours. Thus, the effect of deuterium is not a simple one. Further human studies would hopefully add clarity, but it seems there are many factors to be taken into account if choosing deuterium concentration. What is evident is that even if you decide on deuterium depletion, there is a goldilocks zone.
Overall, the body of evidence currently appears promising but inadequate. A moderate deuterium depletion of water may assist some in cancer treatment, in improving cell metabolism, growth and repair, improving our brains, and protecting organs such as our heart.
Have you tried Deuterium Depleted Water? If so, let us know your verdict!
References
Basov, A.; Fedulova, L.; Baryshev, M.; Dzhimak, S. Deuterium-Depleted Water Influence on the Isotope 2H/1H Regulation in Body and Individual Adaptation. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1903.
Gyöngyi, Zoltán & Budán, Ferenc & Szabó, István & Ember, István & Kiss, Istvan & Krempels, Krisztina & Somlyai, Ildikó & Somlyai, Gábor. (2013). Deuterium Depleted Water Effects on Survival of Lung Cancer Patients and Expression of Kras, Bcl2, and Myc Genes in Mouse Lung. Nutrition and cancer. 65. 240-6. 10.1080/01635581.2013.756533.
Lia, H. Yub, C., Wang, F., Changa, S.J., Yaob, J., and Blake R.E. (2016). Probing the metabolic water contribution to intracellular water using oxygen isotope ratios of PO4. PNAS, 113 5862–5867. doi/10.1073/pnas.1521038113
Li, X., & Snyder, M. P. (2016). Can heavy isotopes increase lifespan? Studies of relative abundance in various organisms reveal chemical perspectives on aging. BioEssays : news and reviews in molecular, cellular and developmental biology, 38(11), 1093–1101. doi:10.1002/bies.201600040
Mladin, C., Ciobica, A., Lefter, R., Popescu, A., and Bild, W.. (2014). Deuterium depletion induces anxiolytic-like effects in rats. Archives of Biological Sciences. 66. 947-953. 10.2298/ABS1402947M.
Rehakova, R. & Klimentova, J. & Cebová, Martina & Barta, A. & Matuskova, Z. & Labas, P. & Pechanova, O.. (2016). Effect of deuterium-depleted water on selected cardiometabolic parameters in fructose-treated rats. Physiological research. 65. S401-S407.
Somlyai, G., Javaheri, B., Davari, H., Gyöngyi, Z., Somlyai, I., Tamaddon, K., Boros, L. (2016). Pre-Clinical and Clinical Data Confirm the Anticancer Effect of Deuterium Depletion. Biomacromolecular Journal, 2(1), 1-7
Strekalova, T., Evans, M., Chernopiatko, A., Couch, Y., Costa-Nunes, J., Cespuglio, R., Chesson, L., Vignisse, J., Steinbusch, H.W., Anthony, D.C., Pomytkin, I., and Lesch, K. (2015)
Deuterium content of water increases depression susceptibility: The potential role of a serotonin-related mechanism. Behavioural Brain Research 277, 237-244 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2014.07.039.
Syroeshkin, A.V., Antipova, N.V., Zlatska, A.V., Zlatskiy, I.A., Skylska, M.D., Grebennikova, T.V., and Goncharuk, V.V. (2018) The effect of the deuterium depleted water on the biological activity of the eukaryotic cells. Journal of Trace Elements in Medicine and Biology, 50, 629-633, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtemb.2018.05.004.
Zhang, X., Gaetani, M., Chernobrovkin, A., and Zubarev, R.A. (2019) Anticancer Effect of Deuterium Depleted Water- Redox Disbalance Leads to Oxidative Stress. Molecular & Cellular Proteomics, 18 (12) 2373-2387; doi: 10.1074/mcp.RA119.001455
Zlatska, A., Gordiienko, I., Vasyliev, R. et al. (2018). In Vitro Study of Deuterium Effect on Biological Properties of Human Cultured Adipose-Derived Stem Cells. The Scientific World Journal, vol 2018. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/5454367.
刘宏建高恒杨国华 (2014). Patent number CN203833608. Deuterium-depleted water producing system. Retrieved from https://patents.google.com/patent/CN203833608U/en608uN203833608U

hi, your style is very good.Following your news.
Thanks Rory, we really value your feedback. What specifically did you enjoy about this article?